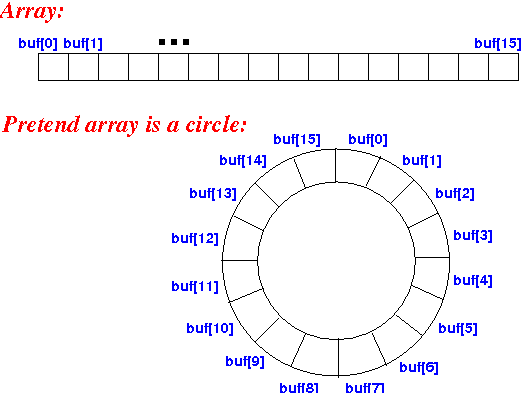
- Circular array:
- Circular array =
a data structure that
used a array as if it
were
connected end-to-end
Schematically:
- This data structure
is also known as:
- Circular buffer
- Cyclic buffer
- Ring buffer
- Circular array =
a data structure that
used a array as if it
were
connected end-to-end
- A circular buffer has
2 "pointers" (or
indices):

- Read pointer: (or read position)
- Read pointer =
the index of the
circular array used by
a read operation
Example:
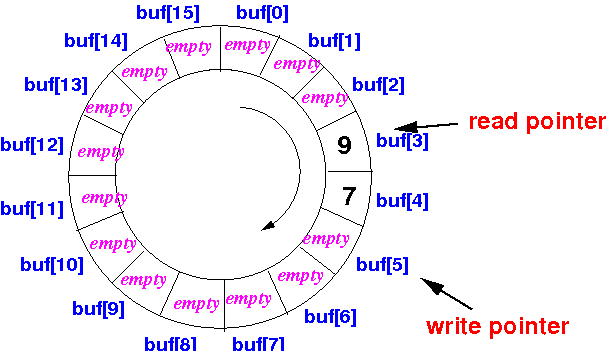
- In the above figure, a
read operation will
return the
value 9 in
buf[2]
(because the read pointer read = 2)
- In the above figure, a
read operation will
return the
value 9 in
buf[2]
- Read pointer =
the index of the
circular array used by
a read operation
- Read pointer: (or write position)
- Write pointer =
the index of the
circular array used by
a write operation
Example:
- In the above figure, a
write operation will
update the
array element
buf[7]
(because the write pointer write = 7)
- In the above figure, a
write operation will
update the
array element
buf[7]
- Write pointer =
the index of the
circular array used by
a write operation
- Fact:
- The read and
write operations will
advance their
corresponding pointers
(Because you don't want the read and write operations to read/write the same array element over and over again....)
- The read and
write operations will
advance their
corresponding pointers
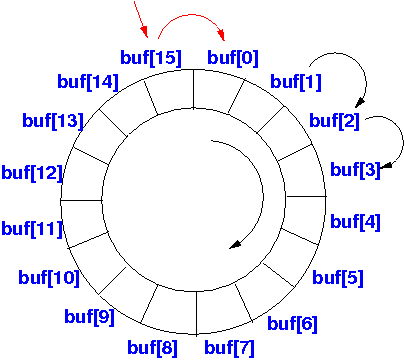
- The read/write pointers in the
following circular array:

will advance in the following manner:
- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 0, 1, 2, 3, .... and so on...
because the indices will wrap around:
- It is very easy to
increase an index in a
wrap around manner:
index = (index + 1) % N where N = the number of indicesExample:
read = (read + 1) % 4 // will increase read as: // 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, ...
- The read operation on a
circular array is
as follows:
DataType read() { DataType r; // Variable used to save the return value r = buf[read]; // Save return value read = (read+1)%(buf.length); // Advance the read pointer return r; }
- The write operation on a
circular array is
as follows:
void write(DataType x) { buf[write] = x; // Store x in buf at write pointer write = (write+1)%(buf.length); // Advance the write pointer }
- To discover
how to represent an
empty circular buffer:
- Let's find out how the information changes when we read data from a circular buffer first....
- The following diagram depicts a
circular buffer (array) with
3 data items:

- After reading
one data item, the
circular buffer (array) will contain
2 data items:
- After reading
two more data item, the
circular buffer (array) will become
empty:
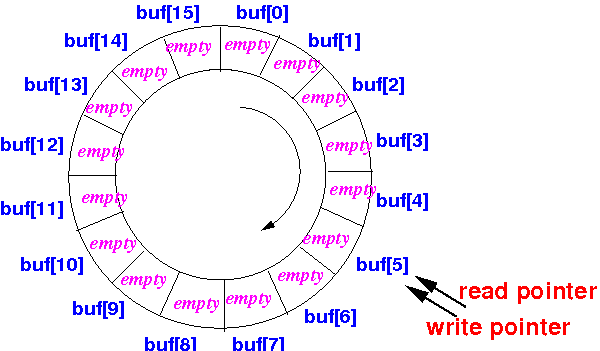
Therefore, a circular array (buffer) is empty if:
read pointer == write pointer
- To discover
how to represent an
empty circular buffer:
- Let's find out how the information changes when we write data into a circular buffer first....
- The following diagram depicts a
circular buffer (array) with
2 empty slots:
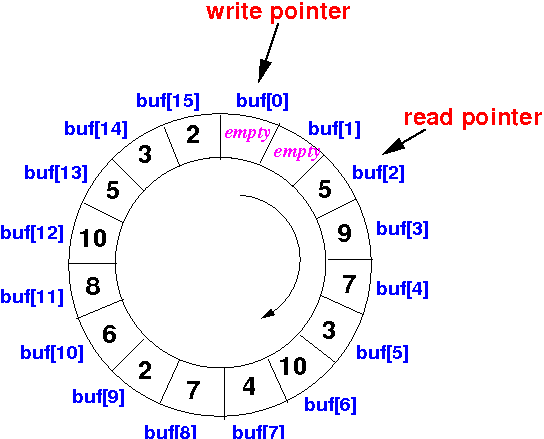
- After writing
one data item, the
circular buffer (array) will contain
1 empty slot:

- After writing
another data item, the
circular buffer (array) will become
full:
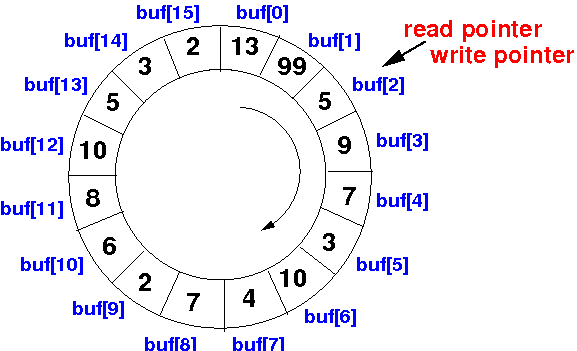
Therefore, a circular array (buffer) is full if:
read pointer == write pointer
- Trouble:
- The condition
read pointer == write pointer
can indicate:
- an empty buffer, or
- a full buffer
- The condition
read pointer == write pointer
can indicate:
- Traditionally, the following
trick is used
to to break
the ambiguity:
- We assume that the
circular buffer
is full when:
- There is one empty slot left in the circular buffer:
Example:
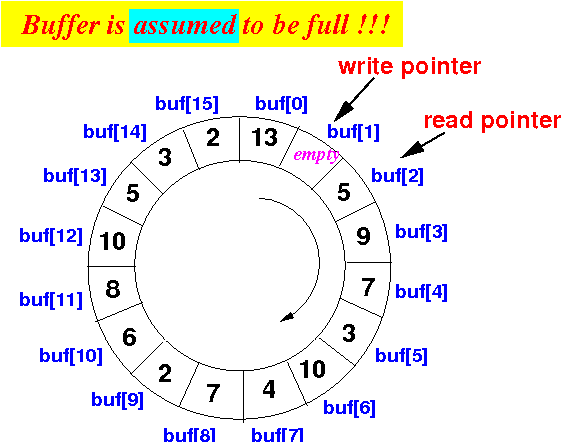
In other words, we use the following test to check if the circular buffer is full:
read pointer == ( write pointer + 1 ) % (buf.length) - We assume that the
circular buffer
is full when:
- Just like the Stack,
we can implement a
Queue using
different data structures.
You just saw the implementation of the queue using a list
- The implementation of
operations of a queue using
a circular array is as follows:
enqueue( x ) // This is writing in a circular buffer (See: click here) { if ( read == ( write + 1 ) % (buf.length) ) { throw new Exception("Queue is full"); } buf[write] = x; // Store x in buf at write pointer write = (write+1)%(buf.length); // Advance the write pointer }
DataType dequeue() // This is reading in a circular buffer (See: click here) { DataType r; // Variable used to save the return value if ( read == write ) { throw new Exception("Queue is empty"); } r = buf[read]; // Save return value read = (read+1)%(buf.length); // Advance the read pointer return r; }
- In Java:
public class ArrayQueue implements Queue { /* ========================================== Node "inner class" ========================================== */ public class Node { double value; Node next; public Node( double x ) { value = x; next = null; } public String toString() { return "" + value; } } public double[] buf; // Circular buffer public int read, write; // read and write pointers // Constructor public ArrayQueue(int size) { buf = new double[size]; // Create array for circular buffer read = 0; // Initialized read & write pointers write = 0; } /* ==================================================== enqueue(x ): ==================================================== */ public void enqueue( double x ) throws Exception { if ( read == ( write + 1 ) % (buf.length) ) // Full... { throw new Exception("Queue is full"); } buf[write] = x; // Store x in buf at write pointer write = (write+1)%(buf.length); // Advance the write pointer } /* ==================================================== dequeue(): ==================================================== */ public double dequeue( ) throws Exception { double r; // Variable used to save the return value if ( read == write ) { throw new Exception("Queue is empty"); } r = buf[read]; // Save return value read = (read+1)%(buf.length); // Advance the read pointer return r; } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The Queue interface Prog file: click here
- The ArrayQueue implementation Prog file: click here
- The test Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac testProg.java
- To run: java testProg
- The following test program can
be used to trigger a
queue full error:
public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception { Queue myQ = new ArrayQueue(3); double x; myQ.enqueue(1.0); System.out.println("enqueue(1.0): " + "myQ = " + myQ); myQ.enqueue(2.0); System.out.println("enqueue(2.0): " + "myQ = " + myQ); myQ.enqueue(3.0); // <--- will cause exception System.out.println("enqueue(3.0): " + "myQ = " + myQ); }
- The following test program can
be used to trigger a
queue empty error:
public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception { Queue myQ = new ArrayQueue(10); double x; x = myQ.dequeue(); // <--- will cause exception }