- public
- public members
(variables and methods) are
accessible in
every method of
every class
I.e.: the world.
- public members
(variables and methods) are
accessible in
every method of
every class
- private
- private members
(variables and methods) are
accessible in
methods in the
defining class
I.e.: the class where the member is defined.
- private members
(variables and methods) are
accessible in
methods in the
defining class
- Default access specifier:
- If an instance member (variable or method) or a class member (variable or method) is defined without any access specfier, the member has the default access specifier
- Example:
package myLib; public class ClassA { /* ---------------------------------------- Default (no access specfier) access ---------------------------------------- */ static void Method81() { System.out.println( "*** This is (no specifier) Method81() of ClassA in PACKAGE myLib"); } }
- Meaning of the
default access speficier:
- default access specifier
(no specifier used):
package access
- default (package) access members
are accessible by statement in methods that are
contained
inside:
- the defining class
(= the class that contains the variable or method with default access)
- Any class inside the same package as the defining class
- the defining class
(= the class that contains the variable or method with default access)
- default access specifier
(no specifier used):
package access
- Experiment 1:
- Show accessing Method81() from a class that is not inside package myLib is not permitted
We will set up the following scenario:
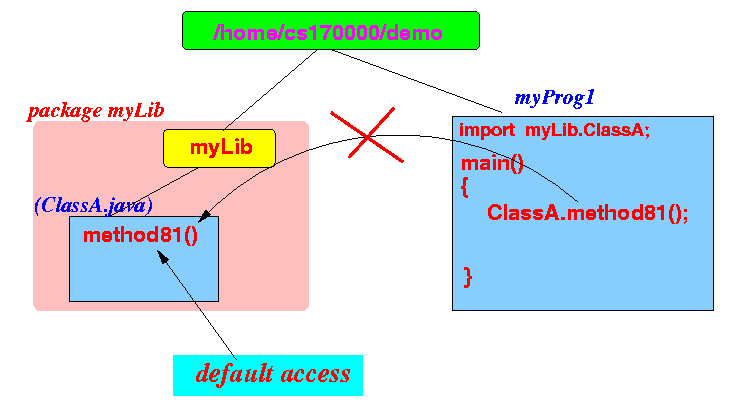
The method main() in myProg1.java is not inside package myLib:
/* NOT a class inside package myLib */ import myLib.*; public class myProg1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassA.Method81(); // Try to invoke the PACKAGE access method (fail) } }Result: compile error
>>> javac myProg1.java myProg1.java:9: Method81() is not public in myLib.ClassA; cannot be accessed from outside package ClassA.Method81(); // Try to invoke the PACKAGE access method (fail) ^ 1 error
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The myProg1.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassA.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- mkdir ~/demo
- mkdir ~/demo/myLib
- Right click on link ClassA.java and save ClassA.java in the directory ~/demo/myLib.
- Right click on link
myProg1.java
and
save myProg1.java
in directory ~/demo.
- To compile ClassA.java: (cd ~/demo; javac myLib/ClassA.java)
- To compile myProg1.java:
(cd ~/demo; javac myProg1.java)
- Replace /home/cs170000 with your own home directory !!!
- You will see the error message...
Note:
- I am taking advantage of the fact that "." is the default search path (class path)
- The program file is inside /home/cs170000/demo
- The package myLib is inside the sub-directory myLib inside /home/cs170000/demo
- Experiment 2:
- Show accessing Method81() from a class that is inside package myLib is permitted
We will set up the following scenario:
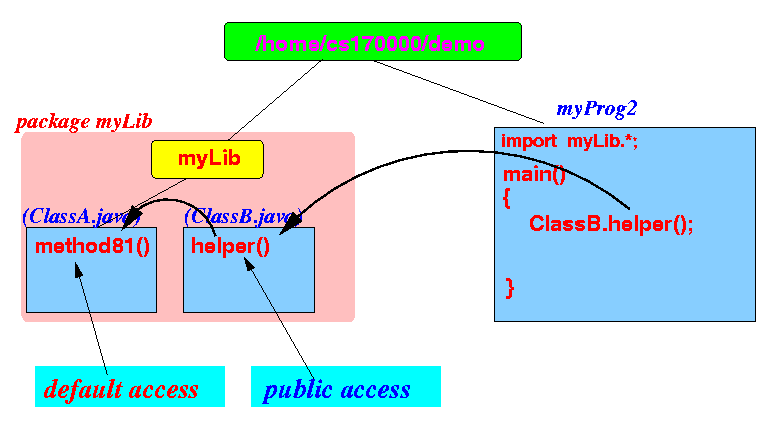
The method helper() inside ClassB is inside package myLib and has public access
package myLib; public class ClassB { /* ------------------------------ PUBLIC access ------------------------------ */ public static void helper() { System.out.println( "*** This is PUBLIC helper() of ClassB in PACKAGE myLib"); System.out.println( "--- I will invoke the PACKAGE access Method81() in ClassA"); ClassA.Method81(); // invoke (default access) method ! } }The method main() will invoke ClassB.helper() (which in turn will invoke ClassA.Method81()):
import myLib.*; public class myProg2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassB.helper();} }Result:
*** This is PUBLIC helper() of ClassB in PACKAGE myLib --- I will invoke the PACKAGE access Method81() in ClassA *** This is (no specifier) Method81() of ClassA in PACKAGE myLib
This experiment shows that the method helper() (that is inside the same package) can invoke the method ClassA.Method81() !!
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The myProg2.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassB.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- mkdir ~/demo
- mkdir ~/demo/myLib
- Right click on link ClassA.java and save ClassA.java in the directory /home/cs170000/demo/myLib.
- Right click on link ClassB.java and save ClassB.java in the directory /home/cs170000/demo/myLib.
- Right click on link
myProg1.java
and
save myProg1.java
in directory /home.cs170000/demo.
- To compile ClassA.java: (cd ~/demo; javac myLib/ClassA.java)
- To compile ClassB.java: (cd ~/demo; javac myLib/ClassB.java)
- To compile myProg1.java:
(cd ~/demo; javac myProg2.java)
- Replace /home/cs170000 with your own home directory !!!
- To run: (cd ~/demo; java myProg2)