- When you develop an algorithm, you want to
make it as useful as possible
- The way the
Selection Sort algorithm is
written:
public class SelSort1 { public static void main(String[] args) { /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- Define the used variables (make sure you have the type correct !) ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 6.7, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements int i, j, min_j; // Array indices double help; // helper variable for 3-way exchange /* --------------------------------------------------- The selection sort algorithm --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i ++ ) { /* --------------------------------------------------- Find array element with min. value among a[i], a[i+1], ..., a[n-1] --------------------------------------------------- */ min_j = i; // Assume elem i (a[i]) is the minimum for ( j = i+1 ; j < a.length ; j++ ) { if ( a[j] < a[min_j] ) { min_j = i; // We found a smaller minimum, update min_j } } /* --------------------------------------------------- Swap a[i] and a[min_j] --------------------------------------------------- */ help = a[i]; a[i] = a[min_j]; a[min_j] = help; } } }Fact:
- The Selection Sort Algorithm will only sort the elements in the array a defined inside the program.
- Suppose we
must sort
2 arrays a and b....
The way the Selection Sort Algorithm is written, we need to do the following to sort 2 arrays a and b:
public class SelSort2 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 6.7, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements double[] b = { 6.7, 4.5, 9.9}; // Second array int i, j, min_j; // Array indices double help; // helper variable for 3-way exchange /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array before sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { System.out.println( a[i] ); } /* --------------------------------------------------- The selection sort algorithm --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { /* --------------------------------------------------- Find array element with min. value among a[i], a[i+1], ..., a[n-1] --------------------------------------------------- */ min_j = i; // Assume elem i (a[i]) is the minimum for ( j = i+1 ; j < a.length ; j++ ) { if ( a[j] < a[min_j] ) { min_j = j; // We found a smaller minimum, update min_j } } /* --------------------------------------------------- Swap a[i] and a[min_j] --------------------------------------------------- */ help = a[i]; a[i] = a[min_j]; a[min_j] = help; } System.out.println( "Array after Selection Sort:"); /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array after sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { System.out.println( a[i] ); } /* ============= Sort array b ================= */ System.out.println(); /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array before sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < b.length ; i ++ ) { System.out.println( b[i] ); } /* --------------------------------------------------- The selection sort algorithm --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < b.length ; i++ ) { /* --------------------------------------------------- Find array element with min. value among b[i], b[i+1], ..., b[n-1] --------------------------------------------------- */ min_j = i; // Assume elem i (b[i]) is the minimum for ( j = min_j+1 ; j < b.length ; j++ ) { if ( b[j] < b[min_j] ) { min_j = j; // We found a smaller minimum, update min_j } } System.out.println("i = " + i + ", min-index = " + min_j ); /* --------------------------------------------------- Swap b[i] and b[min_j] --------------------------------------------------- */ help = b[i]; b[i] = b[min_j]; b[min_j] = help; } System.out.println( "Array after Selection Sort:"); /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array after sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < b.length ; i ++ ) { System.out.println( b[i] ); } } }Conclusion:
- It is not practical to use the Selection Sort Algorithm in the present form
- Key to making computer algorithms
more available:
- Package an algorithm in a way that it can operate as independently as possible
- The black box concept:
- In science and engineering, a
black box
is a system which can be viewed
solely
in terms of its
input, output and transfer characteristics
without any knowledge
of its internal workings.
In other words: the details of the implementation is "opaque" (black).

Wikipedia link: click here
- In science and engineering, a
black box
is a system which can be viewed
solely
in terms of its
input, output and transfer characteristics
without any knowledge
of its internal workings.
- A black box in Computer Science is implemented as a method whose functionality (operational characteristics) is completely determined by its input parameters
- The mechanism to making a
black box in
programming is: a method
- Example:
- A blackbox (oracle) that
computes the square of its
input:
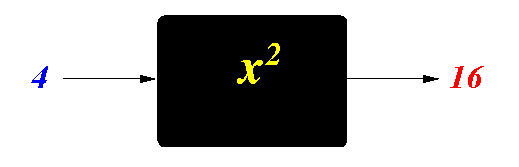
- How this blackbox is
implemented as a
Java method:
public static double Square( double x ) { double out; out = x * x; // Body of method performs the operation return ( out ); // Output }
- A blackbox (oracle) that
computes the square of its
input:
- Notice that:
- The input(s) are provided
to the method through is
parameter variables
- The output is returned by the method through a return statement
- The input(s) are provided
to the method through is
parameter variables
- There are two mechanisms
to convey input information
into a method:
- Information can be passed
into
a method using
then parameter variable(s) of the method.
- Information can be passed into a method using some globally accessible variable(s) that is accessible from within the method.
- Information can be passed
into
a method using
then parameter variable(s) of the method.
-
Passing information
into a method using
parameter variable(s) of the method
- We have been using this mechanism all the time....
Example:
public class Input1 { /* ------------------------------------------------------- Pass information to method with parameter variable x ------------------------------------------------------- */ public static double Square( double x ) { double out; out = x * x; // x contains input information return(out); } public static void main( String[] args ) { double a, b; a = 4.0; b = Square( a ); // The value in a is passed to the parameter var x System.out.println( b) ; } }
Example Program: (Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Input1.java
- To run: java Input1
-
Passing information
into
a method using
some globally accessible variable(s)
that is accessible from within the method.
- A class variable in Java is a globally accessible variable
Example:
public class Input2 { /* ------------------------------------------------------- Pass information to method with class variable x ------------------------------------------------------- */ public static double x; /* ---------------------------------------------------------- Notice that the method does not have any parameter var ! ---------------------------------------------------------- */ public static double Square( ) { double out; out = x * x; // x contains input information return(out); } public static void main( String[] args ) { double a, b; a = 4.0; x = a; // The value in a is passed using class var x b = Square( ); System.out.println( b) ; } }
Example Program: (Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Input2.java
- To run: java Input2
- There are three mechanisms
available
to convey outputs from a method:
- Information stored inside a method can be
returned using a
return statement
- Information stored inside a method can be
returned using a
globally accessible variable
- Information stored inside a method can be returned using a parameter variable that must be passed by reference.
- Information stored inside a method can be
returned using a
return statement
-
Returning information stored inside a method using a
return statement
- We have seen several examples of this already....
Example: (Java)
public class Output1 { /* ------------------------------------------------------- Pass information out of method with RETURN statement ------------------------------------------------------- */ public static double Square( double x ) { double out; // out contains some info. inside method out = x * x; return(out); // Info. in out is returned (passed outside) } public static void main( String[] args ) { double a, b; a = 4.0; b = Square( a ); // The return value is saved in b System.out.println( b) ; } }This mechanism is (trivially) available in Java
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Output1.java
- To run: java Output1
-
Passing information
out of
a method using
some globally accessible variable(s)
that is accessible from within the method.
- Again, we use a class variable in Java which is a globally accessible variable
Example:
public class Output2 { /* ------------------------------------------------------- Pass information out of method with CLASS variable ------------------------------------------------------- */ public static double out; public static void Square( double x ) { out = x * x; // Store the result in CLASS var "out" } public static void main( String[] args ) { double a, b; a = 4.0; Square( a ); // The return value is saved in CLASS var out b = out; // Get the result ! System.out.println( b) ; } }
Example Program: (Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Output2.java
- To run: java Output2
-
Passing information
out of
a method using an
passed-by-reference
parameter variable
- This mechanism is generally available in C/C++
- In Java, this mechanism will only work with reference typed parameter variables (such as arrays)
Example: (C++)
void Square( double & out, double x ) { out = x * x; // Store result in output variable } int main(int argc, char ** argv ) { double a, b; a = 4.0; Square( b, a ); // b is passed by reference and can be modified by // the method so that the result can be returned cout << "a = " << a << " --- squared = " << b << endl; }
- Example Program: (Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: g++ OutputParam.C
- To run: a.out
Note:
- This mechanism is available in Java only when the parameter variable is a object reference variable (such as an array)
- This mechanism is generally available in C/C++
- Recall that:
click here
- An array parameter
passed to a method consists of
the reference (location) of the
array
- An array parameter variable is an alias of the original array !!!
- When the method uses the array parameter to update the array element of the (passed) array, then the elements in the original array will be updated
- An array parameter
passed to a method consists of
the reference (location) of the
array
- In other words:
- The output mechanism that uses an output parameter variable is available in Java if you use an array variable as parameter variable.
- Input and output to the
Sort method (blackbox):
- Input:
- We will pass the array to be sorted in using an array parameter variable
- Output:
- Since the Java method can also update the array elements, we will use the same array parameter variable to return the sorted array output
- Method header:
public static void SelectionSort( double[] a ) { .... .... }The method does not use a return statement to return the result (because the sorted array will be found in the array variable a)
Therefore, the type of the method is void.
- Input:
- Consider the Selection Sort
Algorithm written in the
following manner:
public class SortingTools { public static void SelectionSort(double[] a) { int i, j, min_j; // Array indices double help; // helper variable for 3-way exchange /* --------------------------------------------------- The selection sort algorithm --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i ++ ) { /* --------------------------------------------------- Find array element with min. value among a[i], a[i+1], ..., a[n-1] --------------------------------------------------- */ min_j = i; // Assume elem i (a[i]) is the minimum for ( j = i+1 ; j < a.length ; j++ ) { if ( a[j] < a[min_j] ) { min_j = j; // We found a smaller minimum, update min_j } } /* --------------------------------------------------- Swap a[i] and a[min_j] --------------------------------------------------- */ help = a[i]; a[i] = a[min_j]; a[min_j] = help; } } }Explanation:
- The method
SortingTools.SelectionSort()
gets the input array paramter a
- The method performs the selection sort
algorithm on the
input array paramter a
Important fact:
- Because an array parameter variable is an alias of the original array, the elements in the original array are being sorted !!!
- When it finishes, the original array will become sorted
- The method
SortingTools.SelectionSort()
gets the input array paramter a
- When we have written the
Selection Sort Algorithm
in the above manner,
any user can
now use the Selection Sort algorithm
without knowing exactly
how it works
Example: if I want to sort the arrays a and b , all I need to do is:
public class SelSort3 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 6.7, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements double[] b = { 6.7, 4.5, 9.9}; // Second array int i; /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array before sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { System.out.println( a[i] ); } SortingTools.SelectionSort(a); System.out.println( "Array after Selection Sort:"); /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array after sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { System.out.println( a[i] ); } /* ============= Sort array b ================= */ System.out.println(); /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array before sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < b.length ; i ++ ) { System.out.println( b[i] ); } SortingTools.SelectionSort(b); System.out.println( "Array after Selection Sort:"); /* --------------------------------------------------- Print array after sorting --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( i = 0 ; i < b.length ; i ++ ) { System.out.println( b[i] ); } } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The SortingTools.java Prog file: click here
- The SelSort3.java Prog file: click here
How to run:
- Right click on links and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac SelSort3.java
- To run: java SelSort3
- It is important to understand that the
sorted array must be
conveyed back to the user.
The SelectionSort method can do this because:
- An array parameter variable
is an alias of the
original array variable
Therefore: we can update the original array elements with statements inside the SelectionSort() method
(That's why it works).
- An array parameter variable
is an alias of the
original array variable