- Consider the main method
in the following Java program:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] name = {"John Doe", "Mary Jane", "Peter Pan"}; /* ---------------------------------------------- Print the String array name ---------------------------------------------- */ for ( int i = 0; i < name.length; i++ ) { System.out.println( name[i] ); } } }Notes:
- Notice the
data type of the
parameter variable args of
the main method:
String[] args - Notice that this data type is
the same one as
name:
String[] name
- In other words:
- The data type of the
parameter variable args of
the main method is
an array of String !!!
- args[0] is the
first element of this array.
The data type of a[0] is String - args[1] is the
second element of this array.
The data type of a[1] is String - And so on.
- args.length() is the length of the array.
- The data type of the
parameter variable args of
the main method is
an array of String !!!
- Notice the
data type of the
parameter variable args of
the main method:
- $64,000 question:
- What does the parameter variable args contain ????
- Previously discussed:
(See:
click here)
- Command =
an application program that
is being executed
- Argument = the
words that
follow the command
- Examples:
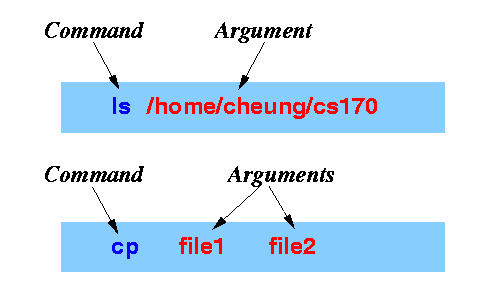
- Command =
an application program that
is being executed
- Fact:
- When we execute a
Java program ProgramName using the following
syntax:
java ProgramName word0 word1 ...
the Java system will pass the words:
- word0 to the first String parameter variable
- word1 to the second String parameter variable
- And so on.
- When we execute a
Java program ProgramName using the following
syntax:
- Graphically explained:
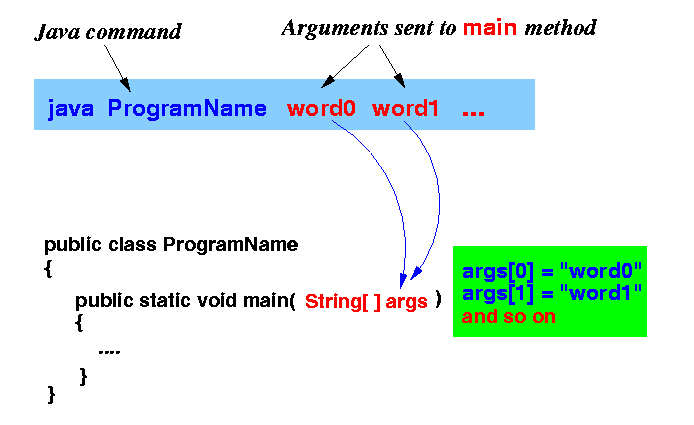
- Java program that prints the elements in the parameter variable
args:
public class Argument1 { public static void main(String[] args) { for ( int i = 0; i < args.length; i++ ) System.out.println( args[i] ); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Argument1.java
- To run: java Argument1
Sample outputs:
UNIX Prompt>> java Argument1 a b c a b c UNIX Prompt>> java Argument1 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
Explanation:
- When the Java program
java Argument1 is
executed, the Java system
first
pass the
command line arguments
(a,
b and
c)
to the main method
- So, when the main method
is executed, it's
parameter variable args
contains:
args[0] = "a" args{1] = "b" args[2] = "c" args.length = 3 - The main method shows the values of its parameter variable by printing them out with a for-statement.
- Problem description:
- Write a Java program that computes the
sum of all its
arguments
Example:
java Sum 1 2 will print 3 java Sum 4 5 8 will print 17 java Sum 2 3 4 5 will print 14
- Write a Java program that computes the
sum of all its
arguments
- We use the running sum algorithm
(see:
click here )
Pseudo code:
sum = 0; for ( every element in args[i] ) do { sum = sum + args[0]; } Print sum;
- Java program:
a failed attempt
public class Sum1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum; int i; sum = 0; // Initialize the running sum for ( i = 0; i < args.length; i++ ) { sum = sum + args[i]; // Add args[i] to running sum } System.out.println( sum ); } }Question:
- Can you spot the error in this program ???
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile:
javac Sum1.java
Error message from the compiler:
Sum1.java:13: incompatible types found : java.lang.String required: int sum = sum + args[i]; ^ 1 error
What is the compiler trying to tell you:
public class Sum1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum; int i; sum = 0; // Initialize the running sum for ( i = 0; i < args.length; i++ ) { sum = sum + args[i]; // Add args[i] to running sum ^^^ ^^^ ^^^^^^^ int int String ** The Java compiler found: int + String ** The compiler requires: int + int } System.out.println( sum ); } }
- Fixing the problem:
- If we want to add,
we must use data types that
are "add-able"
- A String typed value
can not be added
- We must convert a String typed value into an int typed value before we can perform the addition operation !!!
- If we want to add,
we must use data types that
are "add-able"
- A numeric string can be
converted into an
integer using the
parseInt method in
the Integer class.
The parseInt method is invoked as follows:
Integer.parseInt( NumericString )The parseInt method returns an integer value of the numeric string
- Example:
public class ParseInt { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "12"; String b = "34"; System.out.println( a + b ); // a + b = "12" + "34" = "1234" // Because + = concatenate when used on strings System.out.println( Integer.parseInt(a) + Integer.parseInt(b) ); // Integer.parseInt(a) + Integer.parseInt(b) // = Integer.parseInt("12") + Integer.parseInt("34") // = 12 + 34 = 46 // Because + = ADD when used on integers } }Output:
1234 46
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac ParseInt.java
- To run: java ParseInt
- Consider the failed attempt:
public class Sum1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum; int i; sum = 0; // Initialize the running sum for ( i = 0; i < args.length; i++ ) { sum = sum + args[i]; // Add args[i] to running sum ^^^^^^^ We need to convert the String to an integer } System.out.println( sum ); } }
- Corrected program:
public class Sum2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum; int i; sum = 0; // Initialize the running sum for ( i = 0; i < args.length; i++ ) { sum = sum + Integer.parseInt(args[i]); // Add args[i] to running sum } System.out.println( sum ); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Sum2.java
- To run: java Sum2
Example outputs:
cheung@HOME2(17)> java Sum2 1 2 3 cheung@HOME2(18)> java Sum2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 28 cheung@HOME2(20)> java Sum2 3 4 7 14
- A numeric string can be
converted into an
double using the
parseDouble method in
the Double class.
The parseDouble method is invoked as follows:
Double.parseDouble( NumericString )The parseDouble method returns an double precision value of the numeric string
- Example:
public class ParseDouble { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "12.34"; String b = "56.78"; System.out.println( a + b ); // a + b = "12.34" + "56.78" = "12.3456.78" // Because + = concatenate when used on strings System.out.println( Double.parseDouble(a) + Double.parseDouble(b) ); // Double.parseDouble(a) + Double.parseDouble(b) // = Double.parseDouble("12.34") + Double.parseDouble("56.78") // = 12.34 + 56.78 = 69.12 // Because + = ADD when used on doubles } }Output:
12.3456.78 69.12
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac ParseDouble.java
- To run: java ParseDouble
- It is crucial that you
pass correct parameters
to methods
- When you pass a incorrect
parameter to
a method, the result can
range from:
- The method reports back to you that you passed an incorrect value
to:
- The Java program crashes (exits) abruptly
- When you pass a incorrect
parameter to
a method, the result can
range from:
- Warning:
- If the numeric string does
not contain an
integer format number,
the parseDouble method
will cause the Java program to
terminate.
- If the numeric string does not contain a double format number, the parseDouble method will cause the Java program to terminate.
- If the numeric string does
not contain an
integer format number,
the parseDouble method
will cause the Java program to
terminate.
- Example:
public class ParseInt2 { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "12x"; // NOT an integer !!! String b = "34"; System.out.println( a + b ); System.out.println( Integer.parseInt(a) + Integer.parseInt(b) ); // CRASH !!! } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac ParseInt2.java
- To run: java ParseInt2
Output:
cheung@HOME2(26)> java ParseInt2 12x34 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "12x" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:48) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:456) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:497) at ParseInt2.main(ParseInt2.java:12)