- In this webpage, we will apply the
array "traversal" for-statement:
(a is some array (any type) ) int i; for ( i = 0; i < a.length; i++ ) { // statements in the for-loop body will be // executed ONCE for each array element a[i] }to:
- compute the sum of the
elements in an array.
- find the smallest (minimum) value
among the elements in an array.
- find the index of the array element that contains the smallest (minimum) value among the elements in an array.
- compute the sum of the
elements in an array.
- Recall that:
- A computer program (algorithm)
must update some information
while it examines
every possible candidate solution,
and
- The information that the computer program must maintain (update) is problem specific.
Make a note of this when we go through the examples !
- A computer program (algorithm)
must update some information
while it examines
every possible candidate solution,
and
- I will use the
most basic for-statement in
my examples.
- I will not take advantage of any specialized syntax to keep my example as general (applicable to other programming languages) as possible.
- Problem Description:
- We are given a series of
numbers stored inside an array
(say, array a):
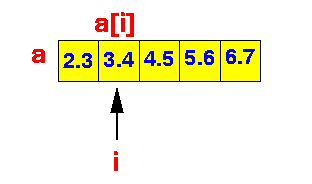
- We must compute the
sum of
all the
values
store in the array a
I.e: compute: 2.3 + 3.4 + 4.5 + 5.6 + 6.7
- We are given a series of
numbers stored inside an array
(say, array a):
- Information that we must maintain:
- sum =
the running sum of the
array elements
- Before any array element
has been added, the
running sum = 0
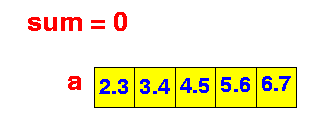
- When we process the
array element a[i],
we add the value a[i]
to the running sum:

(The black arrow represents the array index variable i)
- sum =
the running sum of the
array elements
- Algorithm is Pseudo code:
sum = 0.0; for all elements a[0], a[1], a[2], ... of array a do { add a[i] to sum; } print sum
- Java program:
public class SumArray1 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 6.7, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements int i; // array index double sum; // Running sum for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { sum = sum + a[i]; // Add a[i] to the running sum // Common error: sum = a[i] // This will store a[i] into sum } System.out.println( sum ); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac SumArray1.java
- To run: java SumArray1
- I used an initialized array in
my examples to
simplify the demo
- In real life, you may need to
read in the value from
the user.
- It's easy to change
the program by
adding an input segment
before the
summation algorithm.
- Example:
import java.util.Scanner; public class SumArray2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int n; double[] a; System.out.print("How many numbers in input: "); n = in.nextInt(); // n = # values a = new double[n]; // Create an array of n elements int i; /* ------------------ Read in the values ------------------ */ for ( i = 0; i < a.length; i++ ) { System.out.print("Enter a number: "); a[i] = in.nextDouble(); // Read in number } /* ------------------ Compute the sum ------------------ */ double sum; sum = 0.0; for ( i = 0; i < a.length; i++ ) { sum = sum + a[i]; // Add a[i] to the running sum // Common error: sum = a[i] // This will store a[i] into sum } System.out.println( sum ); } }The program section in red takes care of reading in the input data into the array a
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac SumArray2.java
- To run: java SumArray2
- Problem Description:
- We are given a series of
numbers stored inside an array
(say, array a):
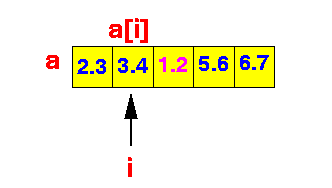
- We must find the
minimum value of
all the
values
store in the array a
I.e: find: 1.2
- We are given a series of
numbers stored inside an array
(say, array a):
- Information that we must maintain:
- min = the current minimum value found among the processed array elements
- Initial attempt
to construct the find minimum
algorithm:
- Before any array element
has been examined, set
min = 0
- When we process the
array element a[i],
we change the minimum to
a[i]
IF:
- a[i] < min
Examples:
- Example 1:
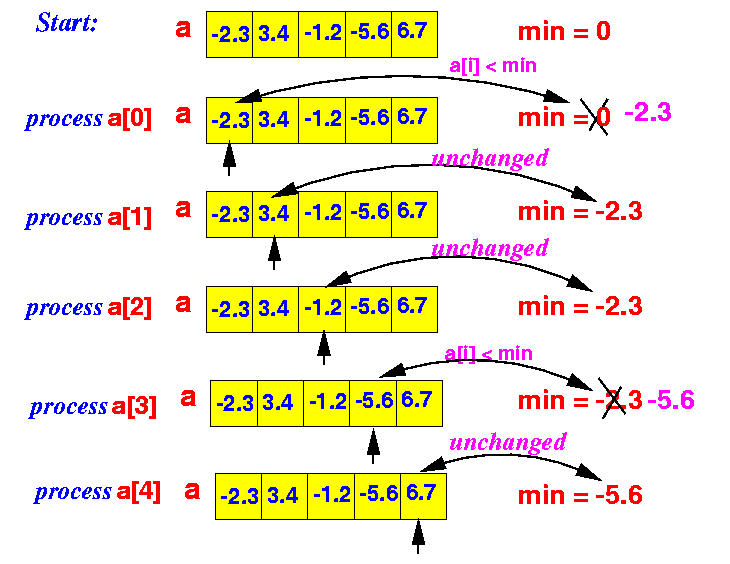
In this example, the algorithm finds the correct minimum value
- Example 2:
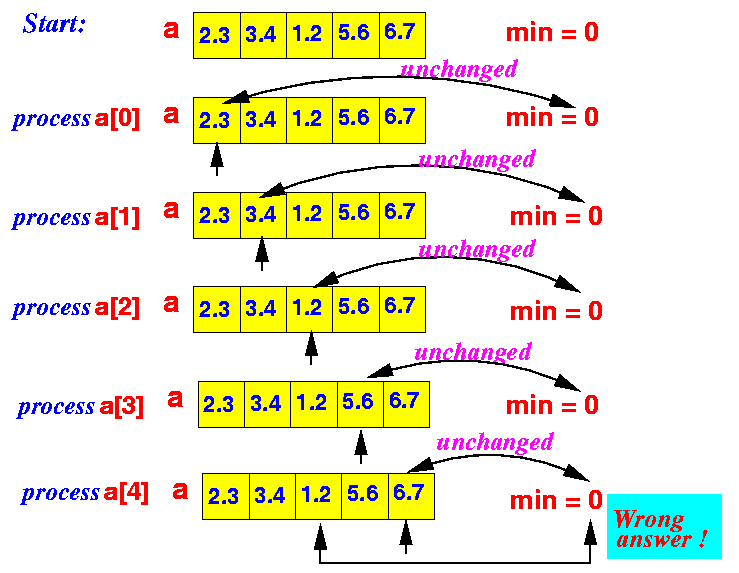
Observation:
- If the initial minimum value (0) is smaller than all the values in the array, the algorithm will find an incorrect minimum value
- Before any array element
has been examined, set
min = 0
- How to correct the problem:
- We need to use a correct initial value
Solution:
- Use a[0] as
the initial minimum value
- Start comparing the array elements from a[1]
Example:
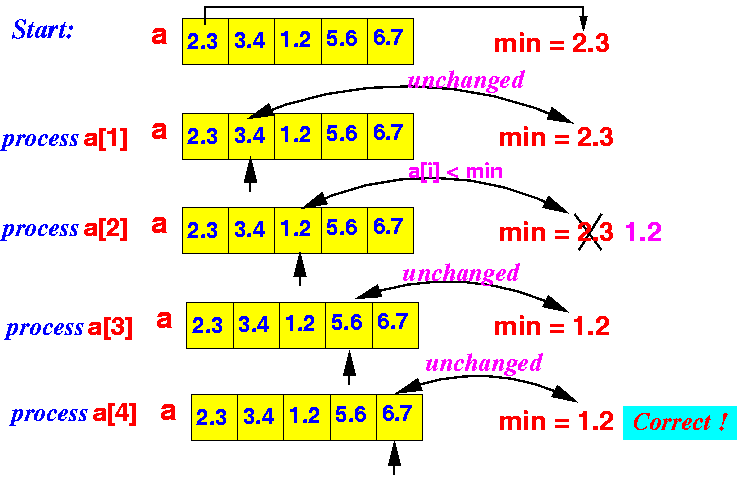
- Algorithm is Pseudo code:
min = a[0]; // Assume a[0] is the minimum for all elements a[1], a[2], ... of array a do { if ( a[i] < min ) { min = a[i]; // We found a smaller minimum } } print min;
- Java program:
public class MinArray1 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 1.2, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements int i; // array index double min; // Current min value min = a[0]; // Initial min. value for ( i = 1 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { if ( a[i] < min ) { min = a[i]; // Found a smaller min. value } } System.out.println( min ); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MinArray1.java
- To run: java MinArray1
- Problem Description:
- We are given a series of
numbers stored inside an array
(say, array a):
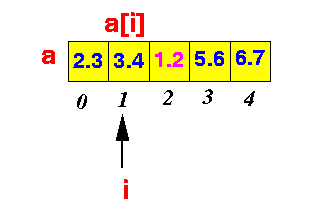
- We must find the
index of the array element
containing the
minimum value of
all the
values
store in the array a
I.e: find: 2
- We are given a series of
numbers stored inside an array
(say, array a):
- Information that we must maintain:
- min_i = the current index of the array element that contains the minimum value found among the processed array elements
- We can modify the
previous algorithm
for finding the
minimum value to solve this problem.
Modified solution:
- Use a[0] as
the initial minimum value
by setting min_i = 0
- Start comparing the array elements
from a[1]
Update min_i when you find a smaller value
Example:
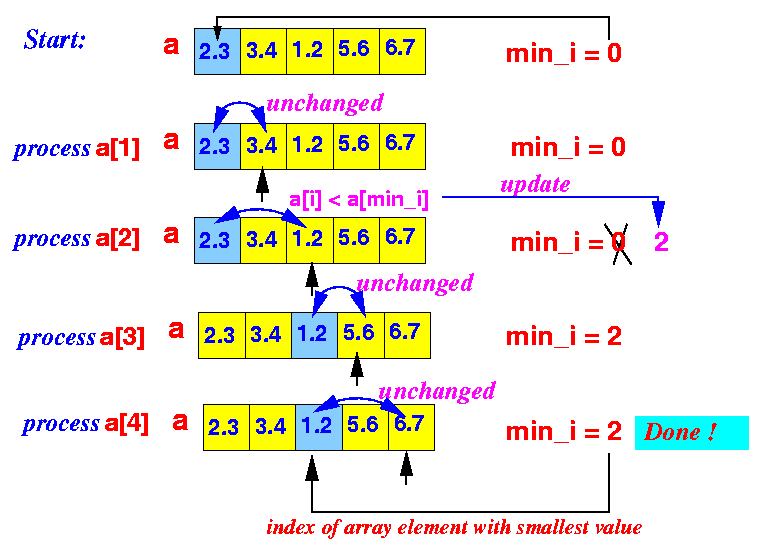
- Use a[0] as
the initial minimum value
by setting min_i = 0
- Algorithm is Pseudo code:
min_i = 0; // Assume elem 0 (a[0]) is the minimum for all element a[1], a[2], ... of array a do { if ( a[i] < a[min_i] ) { min_i = i; // We found a smaller minimum, update min_i } } print min_i;
- Java program:
public class MinArray2 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 1.2, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements int i; // array index int min_i; // Current index with min value min_i = 0; // Assume a[0] is the current min. value for ( i = 1 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { if ( a[i] < a[min_i] ) { min_i = i; // Found a smaller min. value, update min_i } } System.out.println( min_i ); } }Note:
- The variable
min_i is
an integer
(In the previous program, the variable min is a double !)
- The variable
min_i is
an integer
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MinArray2.java
- To run: java MinArray2
- Real world computer programming:
- When you write real world computer applications that process a large amount of data, you need to pay some attention to the efficiency of the computer program.
- Fact on computers in 2011:
- One of the bottle necks
(= the constraining component) of
computers in 2011 is
accessing RAM memory
- The CPU can execute
instructions
much faster than
the memory can fetch them
- You want to write computer programs that uses less access operations to the RAM memory
- One of the bottle necks
(= the constraining component) of
computers in 2011 is
accessing RAM memory
- One of the areas where you can
reduce RAM memory access operations is
in array operations
Facts:
- To access (= read or update) a
simple variable
(such as min),
the computer needs to
access the
RAM memory
once
- To access (= read or update) an
array element
(such as a[i]),
the computer needs to
access the
RAM memory
twice:
- The computer
first need to
access (= read) the
variable i from
RAM memory
(Only after the computer obtained the value of the uses the variable i, it can find out the location of the variable a[i])
- Then the computer need to access (= read or write) the variable a[i]
- The computer
first need to
access (= read) the
variable i from
RAM memory
- To access (= read or update) a
simple variable
(such as min),
the computer needs to
access the
RAM memory
once
- Consider the previous Java program:
public class MinArray2 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 1.2, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements int i; // array index int min_i; // Current index with min value min_i = 0; // Assume a[0] is the current min. value for ( i = 1 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { if ( a[i] < a[min_i] ) // ****** Inefficient ****** { min_i = i; // Found a smaller min. value, update min_i } } System.out.println( min_i ); } }
We can imporve the efficiency by use a simple variable (min) to store a[min_i] and use that variable in the comparison:
public class MinArray3 { public static void main(String[] args) { double[] a = { 2.3, 3.4 , 4.5, 5.6, 1.2, 7.8, 8.9 }; // 7 elements int i; // array index int min_i; // Current index with min value double min; // min = a[min_i] for efficiency min_i = 0; // Assume a[0] is the current min. value min = a[0]; // For efficiency for ( i = 1 ; i < a.length ; i++ ) { if ( a[i] < min ) { min_i = i; // Found a smaller min. value, update min_i min = a[i]; // For efficiency } } System.out.println( min_i ); } }Note:
- We must make certain that
the variable min
contains the value
a[min_i] all the time.
How to achieve this:
- Whenever the variable min_i is updated, we must also update the variable min_i !
- We must make certain that
the variable min
contains the value
a[min_i] all the time.
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MinArray3.java
- To run: java MinArray3