- There are similarities
in make up of
- a class in the Java programming language and
- a book chapter in the English language
that can help you remember the construct of a class
- Here is a graphical depiction of the resemblance:
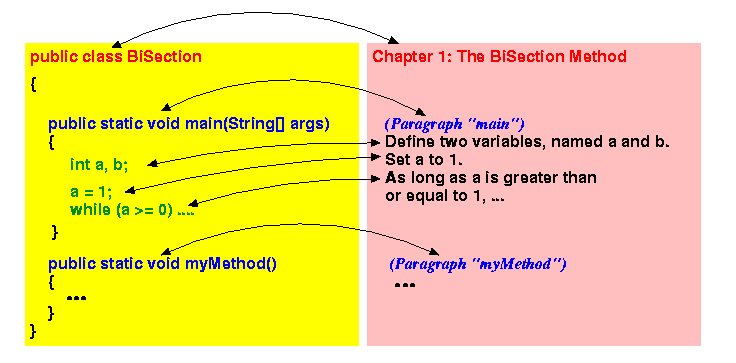
They are similar in the following manner:
Class (in Java) Book Chapter (English) A class contains a number of related methods A chapter contains a number of related paragraphs A method contains a number of statements A paragraph contains a number of sentences A statement is the smallest unit of execution in the Java language A sentence is the smallest unit of readable text in the English language
- Older
(non-object-oriented)
programming languages
have only
one type (kind) of method
-
Newer programming languages
(so called object-oriented languages, explained later)
have
2 types (kinds) of methods:
- Class methods
- Instance methods
- We will now study the
class methods
- We will delay the discussion of the instance methods for later (when we discuss abstract data types).
- Importance of methods:
- Methods can do
more work than
statements:
- A statement can
only
accomplish a very small amount
of work
One single statement cannot solve a complex problem
- A method contains
multiple statements
One single method can solve a complex problem !!!
Therefore, a method is a more useful unit of program execution
- A statement can
only
accomplish a very small amount
of work
- Methods allows us to
build up a
library of useful tools
- You define (describe) a method
once
- Afterwards, you can executed (invoked) the method as many times as you want.
Therefore, we can build up a library of problem solving methods
In fact, the Java library contains a huge amount of useful methods.
E.g., Math.sin(), Math.sqrt(), Scanner methods for input, etc.
- You define (describe) a method
once
- Methods allows us to
solves a complex problem using
the divide and conquer methodology
- In the divide and conquer
problem solving technique,
we break a complex problem/task
into
a number of smaller problems/tasks
- Each of the smaller problem/task is then solved using one method.
- In the divide and conquer
problem solving technique,
we break a complex problem/task
into
a number of smaller problems/tasks
- Methods can do
more work than
statements:
- General rule for using methods:
- When you can discern a well-defined sub-problem/sub-task in the problem/task that you are trying to solve, you solve the sub-problem/sub-task with a method.
- How to use
methods in a
Java program:
-
First,
you must
define the method.
How to define a method:
- Write down the
steps (= statements)
contained in the method.
- Attach a name to the steps (= statements)
Notes:
- You only need to
define
a method
once
(Remember that in Java, you must define the method inside some class.)
- Write down the
steps (= statements)
contained in the method.
- After defining the method,
you can then
call a method
using the name of the method
- When a method is
called,
the statements inside the
corresponding method are
executed
- When all statements in the method has been executed, the execution will resume at the program location of the method call
This mechanism is called method invocation (an older term is procedure call)
Note:
- You can invoke a method as many times as you wish
- When a method is
called,
the statements inside the
corresponding method are
executed
-
First,
you must
define the method.
- We have previously
seen an algorithm to find the
smaller of 2 values
x and
y
(see: click here)
if ( x < y ) { min = x; // x is the smaller value } else { min = y; // y is the smaller value }
- We can create a method to
perform the task of
"finding the minimum of 2 value
as follows:
- Write down the
statements in the
algorithm
- Attach a name (e.g.: min) to the statements
Remember: a method is always contained inside some class in Java
- Write down the
statements in the
algorithm
- Example: defining a method
public class ToolBox // Methods must be contained inside a class { /* ---------------------------------------- A method called "min" that contains the statements to find the smaller of 2 values a and b --------------------------------------- */ public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; if ( a < b ) { m = a; // a is the smaller value } else { m = b; // b is the smaller value } return(m); // Output of the method } ... (You can define more methods inside a class) }Explanation:
- The name of the method
is min
- The method is contained inside
the class named
ToolBox
- The complete name of the
"min" method is:
ToolBox.min
- The name of the method
is min
- Example: using
the method
ToolBox.min:
public class MyProgram { public static void main(String[] args) { double r; r = ToolBox.min( 1.0, 4.0 ); System.out.println(r); r = ToolBox.min( 3.7, -2.9 ); System.out.println(r); r = ToolBox.min( -9.9, 3.8 ); System.out.println(r); } }Notice the advantage of using methods:
- A non-savvy user that wants to
use
the ToolBox.min
method
does not need to know
the statements contained inside the
method ToolBox.min
!!!
- A non-savvy user
will
only need to
know the following
in order to
use the method:
- The (complete) name of the method
(i.e.: ToolBox.min)
- What information the method
needs to do the task
(i.e.: 2 numbers)
- What information the method returns to the user (i.e.: 1 number)
- The (complete) name of the method
(i.e.: ToolBox.min)
- In fact, you were
a non-savvy user of the
methods
in Java's Scanner class
E.g.: You have used nextDouble() without knowing exactly what statements this method contains !
- A non-savvy user that wants to
use
the ToolBox.min
method
does not need to know
the statements contained inside the
method ToolBox.min
!!!
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- File containing the min method: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on
both links and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MyProgram.java
- To run: java MyProgram
Output:
1.0 -2.9 -9.9
A note on the Java compiler:
- The Java compiler can detect that the
program MyProgram.java uses
a method
ToolBox.min from the
class ToolBox
- The Java compiler will try
locate the
file
ToolBox.java
and compile it automatically
- So you do not need to compile the Java program ToolBox.java explicitly --- the Java compiler will do that for you.
- $64,000 Question:
- What happens in a method invocation ???
- We must first explain the
effect of a return statement:
public class ToolBox // Methods must be contained inside a class { /* ---------------------------------------- A method called "min" that contains the statements to find the smaller of 2 values a and b --------------------------------------- */ public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; if ( a < b ) { m = a; // a is the smaller value } else { m = b; // b is the smaller value } return(m); // ****** A "return" statement ******* } ... (You can define more methods inside a class) }
- Syntax of a return statement:
form 1: return ; form 2: return EXPRESSION ;
- Effect of a return statement:
- The return statement is
used to
terminate the execution of
a method.
- When the program executes a
return statement,
the
method terminates (or exits)
- The execution will continue at the location where the method was called
- When the program executes a
return statement,
the
method terminates (or exits)
- If a return statement returns an EXPRESSION, then the value (= result) of the EXPRESSION will be used to replace the method call at the point of call.
- The return statement is
used to
terminate the execution of
a method.
- What happens in a method invocation:
- Java program:
public class MyProgram { public static void main(String[] args) { double r; r = ToolBox.min( 1.0, 4.0 ); // Invokes the "ToolBox.min" method ! System.out.println(r); r = ToolBox.min( 3.7, -2.9 ); System.out.println(r); r = ToolBox.min( -9.9, 3.8 ); System.out.println(r); } } - The ToolBox.min method:
public class ToolBox // Methods must be contained inside a class { /* ---------------------------------------- A method called "min" that contains the statements to find the smaller of 2 values a and b --------------------------------------- */ public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; if ( a < b ) { m = a; // a is the smaller value } else { m = b; // b is the smaller value } return(m); // **** Return statement **** } }
- Execution of the program:
- Program starts executing in the
main method:

- The method invocation
ToolBox.min(1.0, 4.0)
transfers the
program execution to the
method ToolBox.min

- The min method executes
and reaches the
return statement
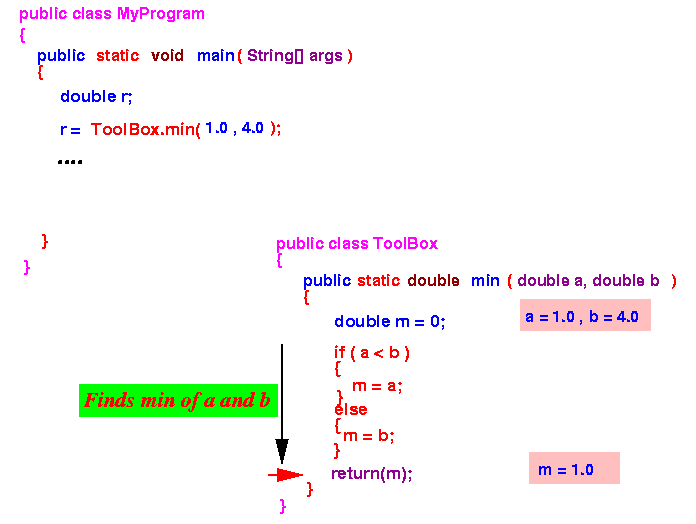
Notice that the variable min = 1.0 when the return statement is executed.
- The return statement
transfers program execution
back to the
point of invocation
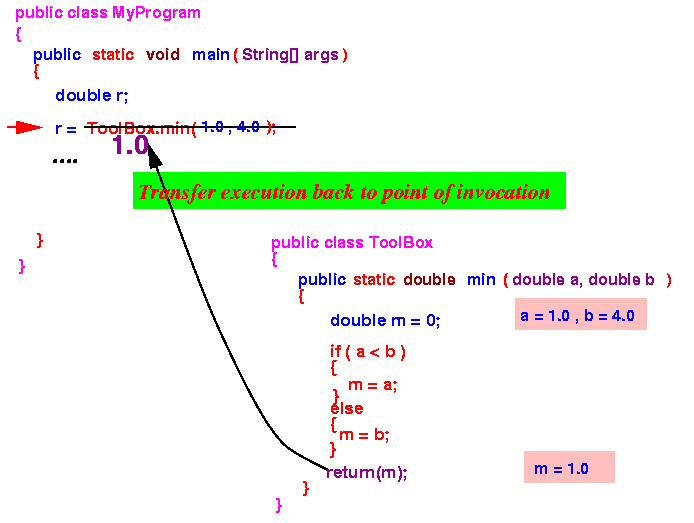
After the method returns, the returned value (1.0) will effectively replace the method invocation
In other words, the assignment statement that will be executed is:
r = 1.0 ;
- Bottom line:
- The variable r will be assigned with the minimum of the 2 values passed to the ToolBox.min method !!!
- Program starts executing in the
main method:
- Java program:
- Syntax used to define a
method:

Note: the construct must appear inside some class, so it will look like this:
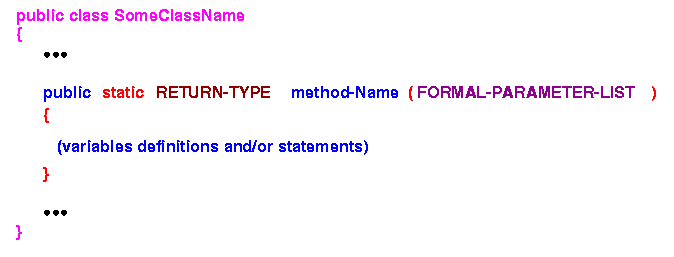
Explanation:
- The keyword public
tells the Java compiler that
we are defining something that had
no access restriction
The "something" can be one of 4 things:
- A method, or
- A variable
- A constant
(final)
- A class (will not be discussed in this course)
In other words, you can only define these 4 kinds of things inside a class
- The keyword static
tells the Java compiler that
we are defining a
class typed
method (or variable).
Note:
- If you omit the keyword static, you will define an instance method or variable or constant which will be discussed later.
- The RETURN-TYPE is a
Jave data type
(e.g., int,
double, etc.)
- The RETURN-TYPE specifies the type of the data that is returned by the method.
- The method-Name is an
identifier that
is used to identify this method.
- You use the method-Name to identify the method in the method invocation
- The pair of brackets
( .... )
tells the Java compiler that
you want to
define
a method.
- You can in fact define 2 different things
inside a class:
- methods
- variables
We will discuss variables defined inside a class later in the course.
- A definition
without the brackets
( ... ) will
define a
variable !!!
- Notice how the Java compiler can
tell the difference:
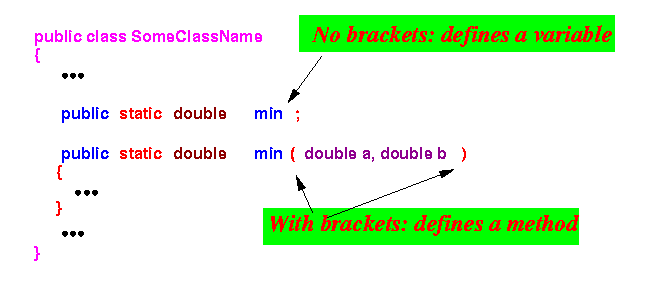
- You can in fact define 2 different things
inside a class:
- The FORMAL-PARAMETER-LIST
is a comma-separated list of
parameter variables
that is passed (= given to) the
method as
additional information
- The items in the
FORMAL-PARAMETER-LIST
has the following form:
TYPE variable-name
- A formal parameter variable
is initialized with the
value given in the method call
It is a way to pass information to the method so it can use the information to perform its designated task
- The items in the
FORMAL-PARAMETER-LIST
has the following form:
- The method body completes the
method definition
The method body is a block (enclosed between { ... })
Within the method body, you can write any number of the following things:
- statements
- variable definitions --- variables defined inside a method body are called local variables
- The method header
- The method header is the
first part of the
method definition without the method body
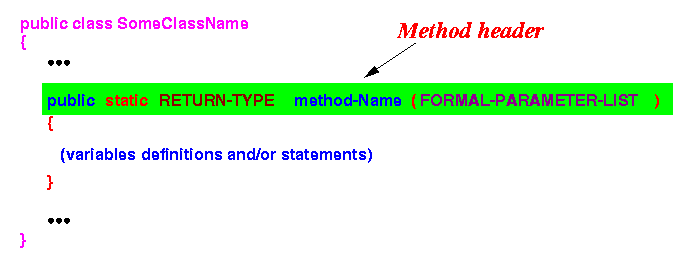
- The method header is the
first part of the
method definition without the method body
- The keyword public
tells the Java compiler that
we are defining something that had
no access restriction
- Example:
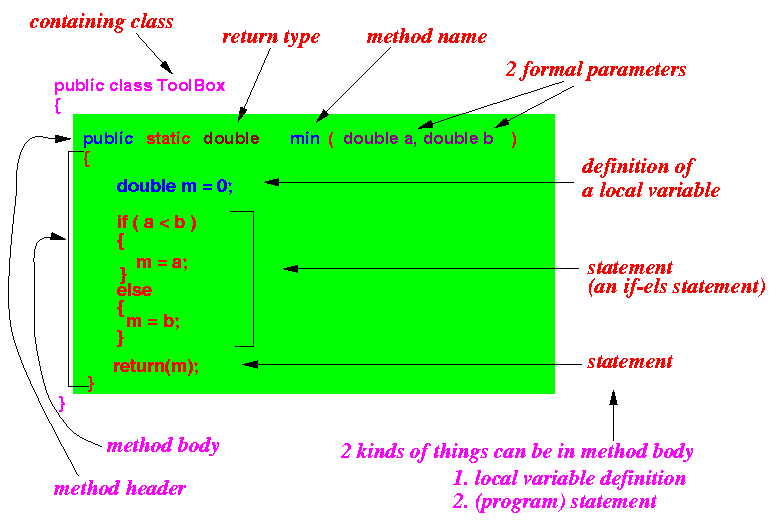
- When you use/invoke a method in your Java program,
the Java compiler will use the following information to
identify which method
you want to use:
- The method name
(i.e., ClassName.MethodName)
- The number and the type of the parameters that you specify in the method invocation.
- The method name
(i.e., ClassName.MethodName)
- Example: suppose we have the follow
2 methods named
min in the same class:
public class ToolBox // contains 2 min methods { /* ---------------------------------------- min with 2 double formal parameters ---------------------------------------- */ public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; System.out.println("You are using min1"); if ( a < b ) m = a; else m = b; return(m); } /* ---------------------------------------- min with 2 int formal parameters ---------------------------------------- */ public static int min ( int a, int b ) { int m = 0; System.out.println("*** You are using min2 !!!"); if ( a < b ) m = a; else m = b; return(m); } }
- Then:
Toolbox.min( 3.0, 1.0 ); // will invoke the first min method Toolbox.min( 3, 1 ); // will invoke the second min method
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on
both links and
save them in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MyProgram.java
- To run: java MyProgram
Output:
>>> java MyProgram You are using min1 1.0 *** You are using min2 !!! 1.0
- Warning:
- If you do not provide the
exact matching types of
parameters, then
the Java compiler will try to
guess (using
safe conversion rules)
which method you want to invoke.
- Example:
ToolBox.min( 3.0, 1 ); // Not 2 int and not 2 double... ToolBox.min( 3, 1.0 ); // Not 2 int and not 2 double...The Java compiler will pick min(double a, double b) because one of the values can be safely converted into double
- If you do not provide the
exact matching types of
parameters, then
the Java compiler will try to
guess (using
safe conversion rules)
which method you want to invoke.
- I recommend that you use
casting to
avoid making the Java compiler to make
the choice for you.
You can do this:
ToolBox.min( 3.0, (double) 1 ); // will use min(double, double) ToolBox.min( (int) 3.0, 1 ); // will use min(int, int)
- In the previous example,
we put the definition of the min method
inside a new class
named ToolBox
- Alternatively, we can
define the
min method
inside the same class as the
main method -
like this:
public class MyProgram { public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; if ( a < b ) { m = a; // a is the smaller value } else { m = b; // b is the smaller value } return(m); // **** Return statement **** } public static void main(String[] args) { double r; r = MyProgran.min( 1.0, 4.0 ); // The name is now: "MyProgram.min" ! System.out.println(r); r = MyProgram.min( 3.7, -2.9 ); System.out.println(r); r = MyProgram.min( -9.9, 3.8 ); System.out.println(r); } }Note:
- Because the definition of
min method is
contained inside the class
MyProgram,
the name
the method is now:
- MyProgram.min
We must use this new name to invoke the min method.
- Because the definition of
min method is
contained inside the class
MyProgram,
the name
the method is now:
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MyProgram.java
- To run: java MyProgram
- Notice that in this example:
public class MyProgram { public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; if ( a < b ) { m = a; // a is the smaller value } else { m = b; // b is the smaller value } return(m); // **** Return statement **** } public static void main(String[] args) { double r; r = MyProgram.min( 1.0, 4.0 ); // The name is now: "MyProgram.min" ! System.out.println(r); r = MyProgram.min( 3.7, -2.9 ); System.out.println(r); r = MyProgram.min( -9.9, 3.8 ); System.out.println(r); } }contains 2 methods
- min
- main
The method main invokes (calls) the method min.
- Short hand method invocation:
- We can reference a method defined inside the same class without using the class name
Example:
public class MyProgram { public static double min ( double a, double b ) { double m = 0; if ( a < b ) { m = a; // a is the smaller value } else { m = b; // b is the smaller value } return(m); // **** Return statement **** } public static void main(String[] args) { double r; r = min( 1.0, 4.0 ); // ****** Shorthand name "min" used System.out.println(r); r = min( 3.7, -2.9 ); System.out.println(r); r = min( -9.9, 3.8 ); System.out.println(r); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac MyProgram.java
- To run: java MyProgram
- Fact:
- A method can be placed in any class
But:
- Imagine placing books on
a number of shelves
- You can place
any book on
any shelf
- Then it very difficult to find a derised book !!!
- You can place
any book on
any shelf
- Advice: to allow
easily location
of methods
- Place related methods
inside the same class
- Give the class a
meaningful name
- Give each method a meaningful name also
- Place related methods
inside the same class
- Example from Java:
- The sin,
cos,
tan,
log,
exp,
sqrt, etc
methods are
all defined inside
the same class
- The name of this class
is Math
- That's why we use:
Math.sqrt( ... )to invoke the sqrt method !!!
- The sin,
cos,
tan,
log,
exp,
sqrt, etc
methods are
all defined inside
the same class
- We still need to discuss some
important topics
related to methods:
- The scope
and lifetime of
local variables
- How parameters are passed to methods.
- The scope
and lifetime of
local variables