- The console is the
terminal window that is
running the Java program
I.e., that's the terminal window where you type in the command java ProgramName
- When a Java program starts running,
the Java runtime system
will
initialize many variables
in support for the running program.
One of these variables is the Java system variable:
System.inwhich represents the console input
The variable System.in is included in every Java program (you don't need to define it).
- A Java program can
obtains inputs
from the console through the
keyboard
In other words:
- The Java system variable System.in represents the keyboard
- At this moment in the course, we want to learn
how to read input from
the keyboard
All you need to know is:
- The variable named System.in represents the keyboard
- It is too early
in the course to
explain the
notation
System.in
- We will explain this after we have covered classes
- Fact:
- There is a lot of work that the computer must do to read in a floating point number
- The details of what the
computer must do to
read in a
number
will be discussed in
CS255
- The Java programming language provides
a
collection
of methods
stored in the
Scanner class
that perform
read operations
(Remember that a class is a container for methods)
- Webpage of the
Java documentation on
Scanner class:
click here

- We will now learn
how to use
the methods in
the Scanner class
to read in
floating point numbers
- The class path of the
Scanner class inside
the Java library is:
java.util.Scanner(see: click here)
- Recall the
Rule of usage of methods in the
Java library:
(See:
click here)
-
If you want to make
a class
inside the Java library
accessible without using
the class path,
a Java program
must first
import
the class
(with an import clause)
- We can use the following
import clause to
import the
Scanner class:
import java.util.Scanner;
- Before a Java program can read input from the keyboard,
the program must
" construct
a
Scanner object
It is too early to explain what this means... I will only tell you how to do it
- A Scanner object
is constructed
using the following statement:
Scanner varName = new Scanner(System.in);
The name varName is an identifier
Example: constructing a Scanner object named in
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- After having constructed
the
Scanner object
named
in,
you can use
the following
expression to
read a floating point number
from the
keyboard:
a = in.nextDouble() ;You must save (store) the number read in by "in.nextDouble()" in a double typed variable with an assignment statement
- What happens inside the computer:
- Just like Math.sqrt(..),
the method call
in.nextDouble() will
invoke (run) a method
in Java's library.
The task performed by in.nextDouble() is to read a floating point number from the keyboard:
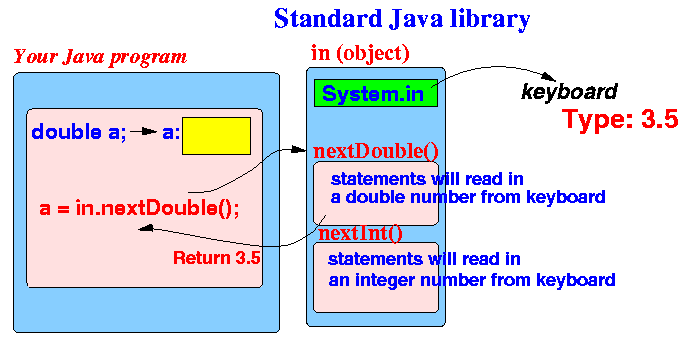
If you type ing "3.5" on the keyboard at the time that in.nextDouble() is running, then the call will return the value 3.5
- The return value will
replace the
method call:

The input value 3.5 is then stored in the variable a !!!
- Just like Math.sqrt(..),
the method call
in.nextDouble() will
invoke (run) a method
in Java's library.
- This figure summarizes
the programming steps to
read in a floating point number:

- Programming Example: ABC formula
import java.util.Scanner; // Import Scanner class (contains methods // for reading keyboard input) public class Abc2 { public static void main(String[] args) { double a, b, c, x1, x2; // Define 5 variable Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); // Construct a Scanner object a = in.nextDouble(); // Read in next number and store in a b = in.nextDouble(); // Read in next number and store in b c = in.nextDouble(); // Read in next number and store in c x1 = ( -b - Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a); x2 = ( -b + Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a); System.out.print("a = "); System.out.println(a); System.out.print("b = "); System.out.println(b); System.out.print("c = "); System.out.println(c); System.out.print("x1 = "); System.out.println(x1); System.out.print("x2 = "); System.out.println(x2); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Abc2.java
- To run: java Abc2
- The previous program works,
but requires the users to
know exactly what to do
In other words:
- An unaware user may not know that he/she needs to enter some input before the program can perform its task.
- Good programming courtesy:
- When the program needs the user to enter input from the keyboard, it must print out a (short) prompt message
- Example:
import java.util.Scanner; // Import Scanner class (contains methods // for reading keyboard input) public class Abc2 { public static void main(String[] args) { double a, b, c, x1, x2; // Define 5 variable Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); // Construct a Scanner object System.out.print("Enter a = "); // ******* Prompt message a = in.nextDouble(); // Read in next number and store in a System.out.print("Enter b = "); b = in.nextDouble(); // Read in next number and store in b System.out.print("Enter c = "); c = in.nextDouble(); // Read in next number and store in c x1 = ( -b - Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a); x2 = ( -b + Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a); System.out.print("a = "); System.out.println(a); System.out.print("b = "); System.out.println(b); System.out.print("c = "); System.out.println(c); System.out.print("x1 = "); System.out.println(x1); System.out.print("x2 = "); System.out.println(x2); } }
- The procedure to
read other types of inputs
from the keyboard is
similar to
the one above.
This one discussed is used to read in a floating point number:

To read in a different kind of item, we need to use a different method in the Scanner class that read the correct type of data.
- Reading an integer number
from the keyboard:
use nextInt()

Note: you also need to use an int typed variable to store an integer value !!!