- Before we can learn to instruct
a computer, we must
first learn to:
- interact with a computer
- Devices used to
interact with a computer:
- Mouse
- Touch pad
- Keyboard
- For casual computer users,
the most important
interaction device is:
- mouse (and a little keyboarding for chatting)...
- For computer programmers,
the most important
interaction device is:
- keyboard !!!
because they must write programs in an English-like programming language
(I dare you to write a book using a mouse by clicking on a virtual keyboard !)
- Preliminary step:
- We must gain authorization
to use the computer system
- This is usually achieve through an authentication process (popularly known as log in process)
- We must gain authorization
to use the computer system
- After log in is successful,
we interact with a computer by:
- Running various computer applications
The application that you need to run depends on the task that you want to perform
Examples:
Task Application Surf the Internet Web browser (such as FireFox, IE, Chrome, etc) Edit a report Text editor (such as Word, gedit, vi, emacs, etc) Email email client (such as Thunderbird) Ledger spreadsheet (such as Microsoft Excel) Database application Database server (such as SQL server)
- Depending on the security setting,
you may need to type a user ID
and the
corresponding password
to
gain access to a PC.
- After this authentication process, you can run applications (usually through some mouse clicks)
- The MathCS computer lab is
located on the
3rd floor of the
MSC building
The lab hours and rules can be found at this webpage: click here
- You can log in
(= gain access) to any
computer in the MathCS lab using:
- your Emory ID
- your Emory password
- Perform this task now:
- Log in to the
computer in front of you
using your
Emory ID and
password
(That's the same as that you use to log in to OPUS)
(If you do not know your ID or password, please tell the Teaching Assistant)
- Log in to the
computer in front of you
using your
Emory ID and
password
- Every computer is
controlled (= "managed") by
a very complex computer program
called
an Operating System (OS)
- The Operating System (OS)
controls:
- The mouse
- The keyboard
- The monitor
- The disks
- ...
- Every component of the computer !!!
- The Operating System (OS) can also:
- Detect mouse clicks
- Detect key strokes
- Load a computer program from hard disk into RAM memory and execute it
- Microsoft Windows
- First developed in 1980
for the IBM-PC by
Microsoft
- Mostly used in PCs
- A history of Windows: http://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows/history
- First developed in 1980
for the IBM-PC by
Microsoft
- UNIX
- First developed in the
early 1970's
for "mini"-computers by
AT&T
(A mini computer is a computer that is less power than a main-frame computer in the 1970's)
- Used in PCs,
and servers
- A history of UNIX: http://www.unix.org/what_is_unix/history_timeline.html
- First developed in the
early 1970's
for "mini"-computers by
AT&T
- MAC OS
- First developed in
1984
for the Macintosh PC by
Apple
- Used in Apple's computers
- A history of MAC OS: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Mac_OS
- First developed in
1984
for the Macintosh PC by
Apple
- Fact about a computer:
- A computer is a
(dumb) machine that
only executes instructions
- If you want a computer to
do a task for you, then you must:
- Give a computer the complete list of instructions that accomplishes the that task
- A computer is a
(dumb) machine that
only executes instructions
- In other words:
making a computer do a task
is
a painful job...
- Fortunately:
- People have written down
the complete list of instructions
to do
frequently performed tasks
- These lists of instructions
have been saved in
computer files
(naturally...)
- These files are
better known as
computer applications
Some well known computer applications:
- Web browser (e.g., Internet Explorer)
- Editor (e.g., Microsoft Word)
- and so on...
- People have written down
the complete list of instructions
to do
frequently performed tasks
- In summary:
- If you want a computer to do a common task, you must run (= "execute") the appropriate application
We will first discuss how to run (execute) an application on a computer
- For PC users, the
most common way to
run a computer program is through
mouse clicks
Example:
- When you want to run
the FireFox web browser,
you double click on
the FireFox icon:

- When you want to run
the FireFox web browser,
you double click on
the FireFox icon:
- This is what is going on inside a computer when you
(double) click on an
icon that is
associated with
a computer program:
- You double click on an
icon
- The Operating System detects
the mouse clicks on the
icon
- The Operating System locates the program that is associated with the icon into RAM and execute it
- You double click on an
icon
- In Microsoft Windows, you can find
out which program is
associated with an icon
by right-click the icon
and select
properties
Example:
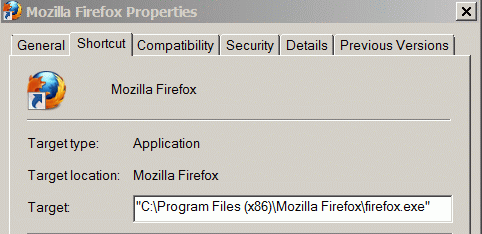
The Target field in the "properties" window shows the path of the program that will be executed when you double click the icon.
- Every computer system
provides an application that
allows the user to
type in the
path of the program that
he/she wants to execute
- Application name:
- Microsoft Windows: cmd (command line tool)
- UNIX: sh (the original Shell), csh (C Shell), ksh (Korn Shell), bash (Born Again Shell),
- MAC OS X: Terminal (it is in fact a UNIX shell program)
- Example: running FireFox
using cmd in
MicroSoft Windows:
- On your PC: click START and run
cmd
- In the cmd window, type
the complete path of
the FireFox application:
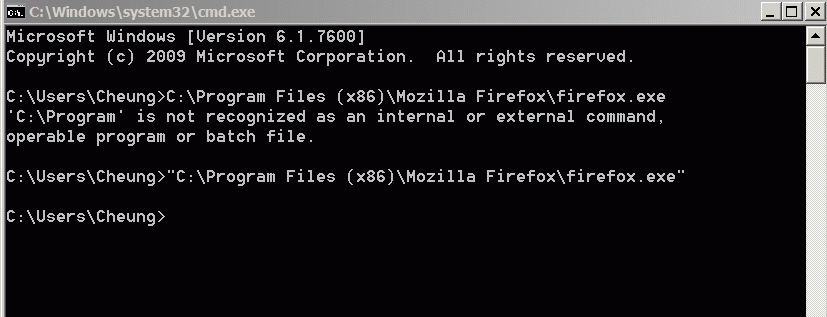
Note: make sure you quote the entire command !!!
- On your PC: click START and run
cmd
- Today,
virtually everyone
has used a computer to write
reports in
high school
- Documents created by computer users are
stored in a computer system
as a:
- computer file
- A computer file is a sequent of
bytes and it can be
readily placed into RAM memory
for processing.
- Most files use the
ASCII encoding method to
represent the characters
- For details on the ASCII encoding, see: AsciiTable.com
- However,
files containing non-English characters
(e.g., Greek letters α, β, etc,
Chinese characters, and so on)
use the
Unicode encoding method.
- For details on the Unicode encoding, see: Unicode.org
- computer file
- A computer file is stored on the hard drive of the computer system
- When you have a small number
(like 10 or so) of
files, you can put the files in
the same location
(e.g., the desk top)
and you can find them back easily
- However, if you have
a large number
(like 1000 or more) of files,
you will have a hard time
locating a file if they are put in one location.
- Directories:
- A directory is
a special file (yep, a directory
is a file) that can contain:
- Information of the locations of files
- Information of the locations of other directories
- A directory is
a special file (yep, a directory
is a file) that can contain:
- Organizing files and directories:
- File and directories are
organized as a
file system
- Every modern file system is organized as a logical tree structure
- File and directories are
organized as a
file system
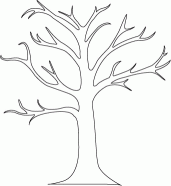
- The shape of a tree looks something like this:
- A
tree structure in
computer science looks like a
"upside-down" tree,
like this:
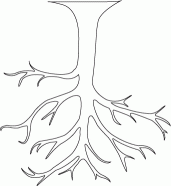
- What a tree structure
in Computer Science look like:
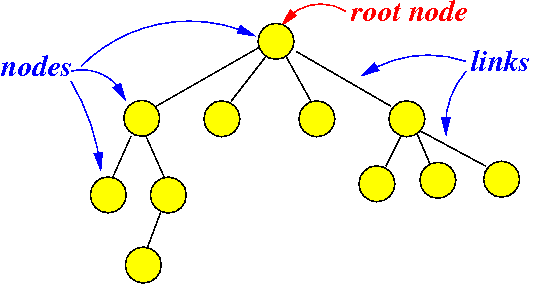
Terminology:
- The circles in the
tree structure are called
nodes
- The top most node in the
tree structure is called the
root node
- The lines in the tree structure are called branches or links
- The circles in the
tree structure are called
nodes
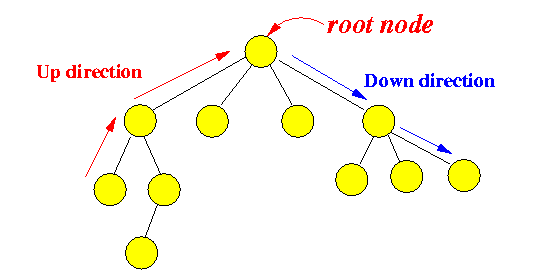
- Directions in the tree:
- Up (or upward direction) =
when you move
from one node to another
(connected) node
that
leads you
closer to the root node
- Down (or downward direction) = when you move from one node to another (connected) node that leads you further away from the root node
Example:
- Up (or upward direction) =
when you move
from one node to another
(connected) node
that
leads you
closer to the root node
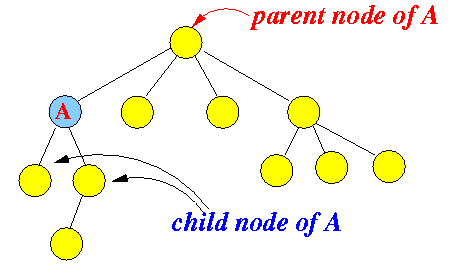
- Parent node:
- Parent node =
the first node that is located in the
upward direction
(There is only one parent node for any node in a tree - look carefully in the picture above.)
- Parent node =
the first node that is located in the
upward direction
- Child node:
- Child node =
any node that is located
immediately in the
downward direction
(There is many child nodes for a node in a tree - look carefully in the picture above.)
Example:
- Child node =
any node that is located
immediately in the
downward direction
- If you have worked with a PC,
you should be familiar with the
Microsoft Windows file system
- The tree structure of the
Microsoft Windows file system is based on the
disk drives that
are available in "your PC"
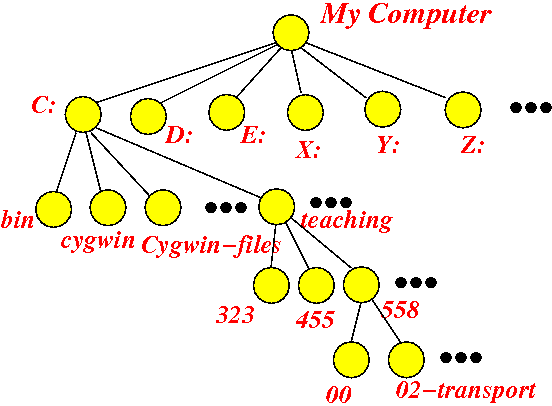
- The root node of the
Microsoft Windows file system is the
node "My Computer"
The first level of branches are the individual disk drives:
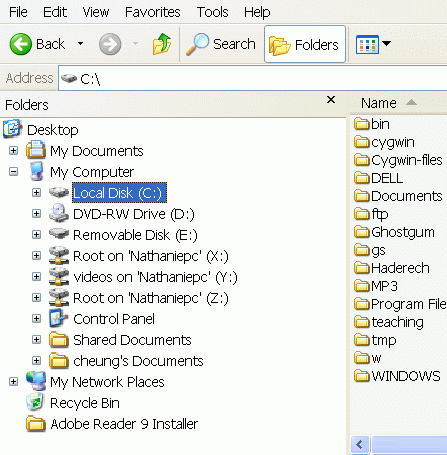
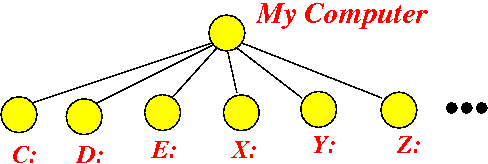
The Local Disk (C:) is a node under the root node (My Computer) that is commonly used to store System and users' files.
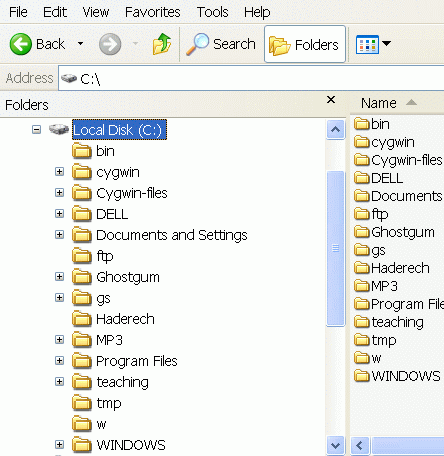
- The following figure
shows the nodes
under the
node Local Disk (C:):
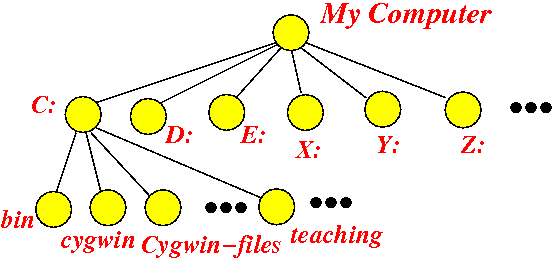
- The following figure shows 2 more levels
of the file system tree structure:
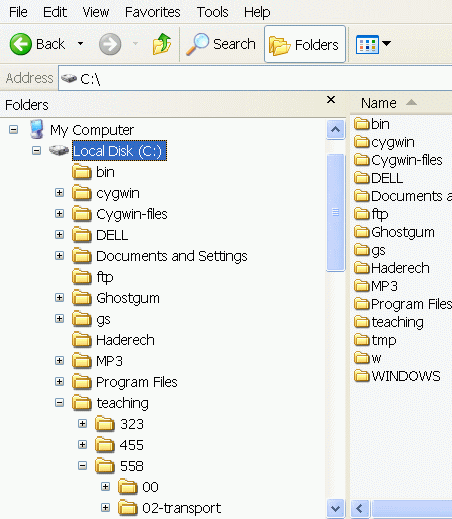
- You will be using the
UNIX Operating System in
college
Reason: UNIX is more stable (crashes less often) (from answer.com - see: click here)

- The tree structure of the UNIX file system:
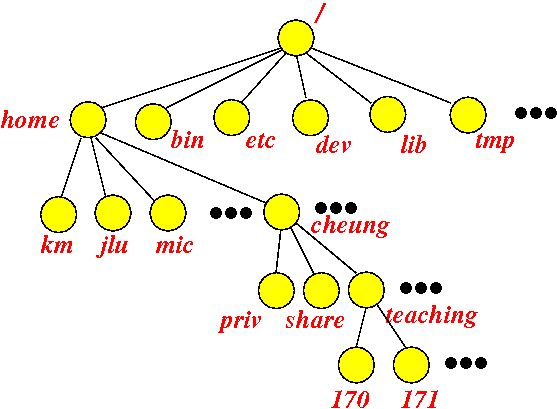
- The tree structure of the
UNIX file system is based on
functionality/purpose:
- Files used for a specific function/purpose is stored in the same directory
- The root node of the
UNIX file system is the
node "/"
- The second level
(immediately under /)
usually contains the
directories:
Directory name Function of files/directories contained in directory home home directories of users bin binary files: files that contain machine instructions dev devices: contains files that link to disk drives, keyboard and other devices lib library files: support files for various high level programming languages tmp temporally files: scratch area for some running programs etc miscellaneous files and directories
- Unlike a PC
("Personal Computer) which is
mainly used by 1 person,
the UNIX operating system is usually used to:
- manage a large computer system that is used by many different users (at the same time)
- Unlike a PC
("Personal Computer) where you can store your files
more or less anywhere
in the file system, you are
assigned a specific location in
the UNIX file system:
- Every user
is assigned a home directory
- You can create (make) new
directories and
files
inside
your home directory
- You cannot create
anything in
someone else's home directory
Nor can you create files/directories in the system's directory (such as: bin, dev, and so on)
- Every user
is assigned a home directory
- The home directories of
all users in the UNIX system are
contained in the home directory
under the root directory:

Example:
- The directory km under home is the home directory of Prof. Mandelberg
- The directory jlu under home is the home directory of Prof. Lu
- And so on...
Each user can create more directories to organize his/her files inside his/her home directory
In the figure, you see some of the some of the directories that Prof. Cheung has created inside his home directory